As we all know, there are many structural types of fiber optic cables. Although they are mostly made from the same bare optical fiber, why are there so many structural types? Next, let us distinguish them in detail.
Types of fiber optic cables suitable for burial
The GYTA53 & GYTY53
Both types of fiber optic cables have a structure with a double-layer PE sheath. Compared with GYTY53, GYTA53 has a layer of aluminum armor inside, and the inner layer of GYTY53‘s water-blocking tape only has an extra layer of PE sheath.
Due to their high tensile and compressive strength, they can be laid directly underneath in relatively mild working conditions. Of course, they still need to be laid through pipes if they are faced with a relatively harsh working environment. The starting point of this structural design is to ensure that the optical signal can still be transmitted normally in the extremely harsh buried environment.
Especially for the fiber optic cable of the GYTA53 structure, since the inner armor layer is wrapped by plastic-coated aluminum tape, we can replace it with plastic-coated steel tape armor according to the customized needs of customers. In this way, the double-layer armor of this optical cable becomes a double-layer plastic-coated steel tape armor, which enables the cable to have higher tensile and impact strength. Correspondingly, its bending performance will be reduced. Of course, these are determined according to the actual use environment. The starting point of the optical cable structure design is to protect the optical bare fibers inside.

Types of fiber optic cables suitable for overhead laying
The GYXTC8S & GYTC8A
These two types of fiber optic cables have a similar “8”-shaped structure, and the upper part of the whole is filled with steel wires to increase the longitudinal tensile strength of the optical cable itself. Due to the complex environment faced by overhead laying and the natural environment such as strong wind, heavy rain, snow, and frost, it is also necessary to consider the distance between the poles of the overhead laying span. In the early stage of engineering design, it is necessary to fully consider the stress that the optical cable will face in the future. Therefore, we can provide different steel wire specifications to fill the optical cable, increase the mechanical properties of the optical cable, and ensure the stability and durability of the transmission.
The structure of the fiber optic cable of GYXTC8S, the structure of the lower part of the fiber optic cable is similar to the structure of the fiber optic cable of GYXTW. It is composed of a loose tube wrapped with a layer of plastic-coated steel strip as the main body. Unlike the GYXTW construction, we usually omit those two parallel wires. Under normal circumstances, there is only one loose tube inside the GYXTC8S, so we recommend that the maximum filling number of its optical bare fibers does not exceed 12 cores. This fiber optic cable is very suitable for communication needs with a small number of overhead cores, so it can not only meet the relatively low cost of fiber optic cable construction but also meet the relatively complex overhead laying conditions.

If the actual number of optical bare fibers required exceeds 12 cores, which types of fiber optic cable should we choose instead? The fiber optic cable of the structure type GYTC8A can meet the needs of the group. Different from GYXTC8S, the entire fiber optic cable part is similar in structure to GYTS. It can be filled with up to 144 cores of optical bare fibers, and there is a steel wire in the central part of the fiber optic cable. Similarly, there is also a layer of plastic-coated steel tape armor on the outside of the loose tube to ensure that the mechanical properties of the optical cable can meet the use standard.

The ADSS
The All Dielectric Self-supporting Aerial Fiber Optic Cable (ADSS) is different from the two cables mentioned above in that it uses aramid yarns instead of metal materials. This allows ADSS to have a lighter weight, which can provide better stability in the case of overhead laying. So, you may be worried that without the metal armor, will it affect its tensile strength? I think this, everyone doesn’t need to worry about the physical properties of aramid. The design starting point of this optical cable is to be suitable for matching with Optical ground wire (OPGW), and its aramid material will not affect the electromagnetic induction generated by electricity, affect power transmission or generate dangerous situations related to strong electricity. The actual status of overhead power lines is taken into full consideration when ADSS cable is being designed. For overhead power lines 10kv and 35kv, PE outer sheath is applied. For power lines 110kV and 220KV, AT outer sheath is applied.

Types of fiber optic cables suitable for pipe laying
The GYTA & GYTS
These two types of fiber optic cables are the most used types in our daily construction. Their design structure is basically the same, the only difference is the difference in armor. GYTA uses plastic-coated aluminum tape armor, while GYTS uses plastic-coated steel tape armor.
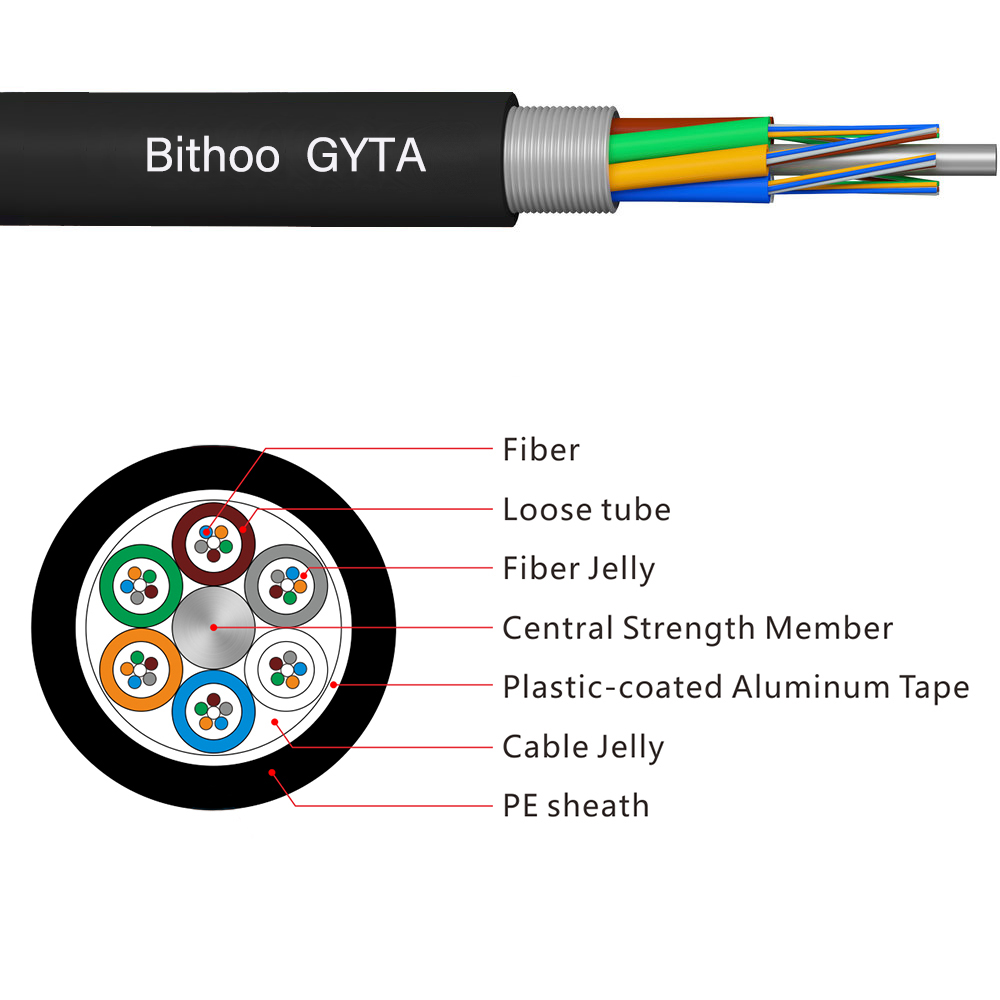
Aluminum tape have a lighter weight and a softer texture. It is easier to construct in the face of relatively complex underground pipelines with many bends. Moreover, the central part has a thicker wire, which ensures that it has better tensile strength.
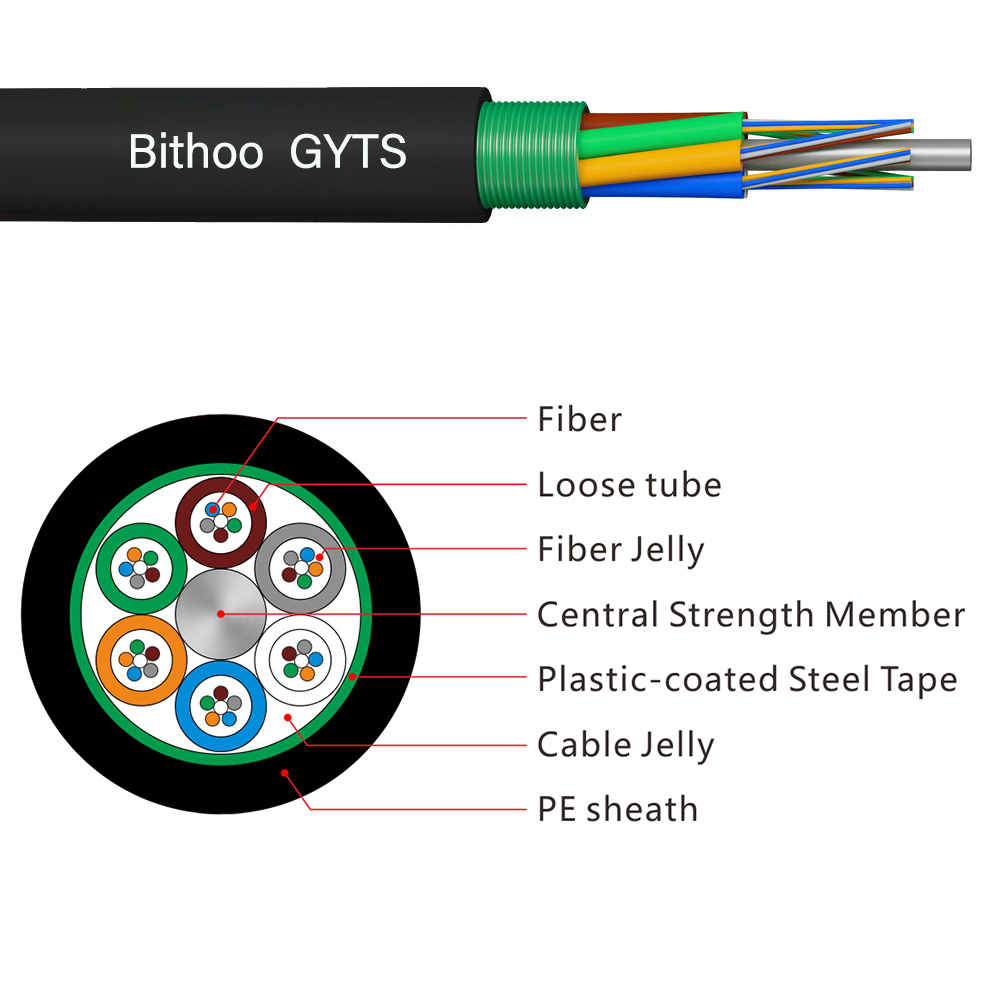
The steel belt has a higher hardness, although it is not as soft as GYTA, but it is more resistant to the accidental occurrence of insects and mice. Therefore, in the case of having outdoor line pipes, these two types of fiber optic cables have very good performance.
GYXTW is a cost-effective fiber optic cable
In many network extension designs, perhaps we do not need to face complex underground pipes, harsh transmission environments, and a large number of optical fiber resources. Then GYXTW is a very ideal choice.

GYXTW has a smaller outer diameter, lighter weight, and also has steel armor and two steel wires. Therefore, it can meet the requirements of laying in wiring pipelines and short-distance overhead laying at the same time. Perhaps, the only downside is that it can only fill up to 12 cores. However, it is a good choice if your fiber optic transmission system does not have many requirements for the number of fibers.
