In communication construction and daily life, WLAN is already a concept we often mention. We will make a detailed description in this article and share it with you regarding the details of WLAN.

Overview of WLAN
WLAN: wireless local area network
The use of wireless connections instead of wired connections is an extension of Ethernet and enriches device connection methods.
A wireless local area network is a local area network formed by at least two devices using wireless connections to establish communication channels.
Usually, a wireless local area network consists of a router and one or more wireless devices that can access the router.
The operation of WLAN is established on the wired network, which is the expansion of the wired network and the change of the terminal access mode and interconnection mode. The basic protocols of Ethernet such as ICMP, DHCP, ARP, TCP, etc., and data forwarding rules are also followed in the WLAN network, and there is no difference.
The WLAN is mainly composed of (Station, STA), (Access Point, AP), (Wireless Medium, WM), and (Distribution System, DS).
Comparison of 2.4GHz and 5GHz
2.4GHz
Advantages: strong signal, small attenuation, strong penetration transmission capability, and long coverage distance;
Disadvantages: Smaller bandwidth, slower speed, susceptible to interference.
5GHz
Advantages: larger bandwidth, faster speed, less interference;
Disadvantages: weak signal, large attenuation, poor penetration and transmission capability, and small coverage distance.
Note: Due to the high frequency of 5G Wi-Fi, the energy of electromagnetic waves is strong, and the penetration ability (invariable direction) is strong. The signal penetration will lose a lot of energy, so the attenuation is relatively large during the propagation process, and the propagation distance is relatively short.
Channel Basic Information
Data transmission medium: electromagnetic wave (carrier wave; propagation speed is the speed of light).
The radio working frequency band used by the wireless network: 2.4GHz/5.8GHz.
Channel: The channel of data transmission in the wireless network, the concept of the frequency domain.
Each channel identifies a certain frequency range, and each channel has a center frequency and a certain bandwidth. Channels are public resources and are fixed and cannot be changed.
2.4GHz frequency band Wi-Fi channel division
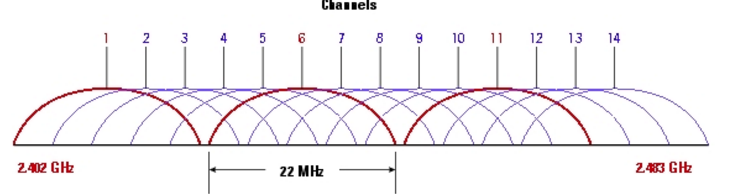
There will be interference between overlapping channels, and the waveform will become higher. Each channel has a center frequency and a certain amount of bandwidth. 14 channels are only supported in Japan.
The effective width of each channel is 20MHz, and there is also a mandatory isolation band of 2MHz (similar to the isolation band on the road). That is, for channel 1 with a center frequency of 2412 MHz, the frequency range of 2401~2423 MHz includes 2, 7, 12; 3, 8, 13; , 9, and 14 are three groups of channels that do not interfere with each other.
Note: When laying out the 2.4GHz wireless network, try to set the adjacent router channels as independent channels or social channels to avoid interference between channels.
5GHz Channel Channeling
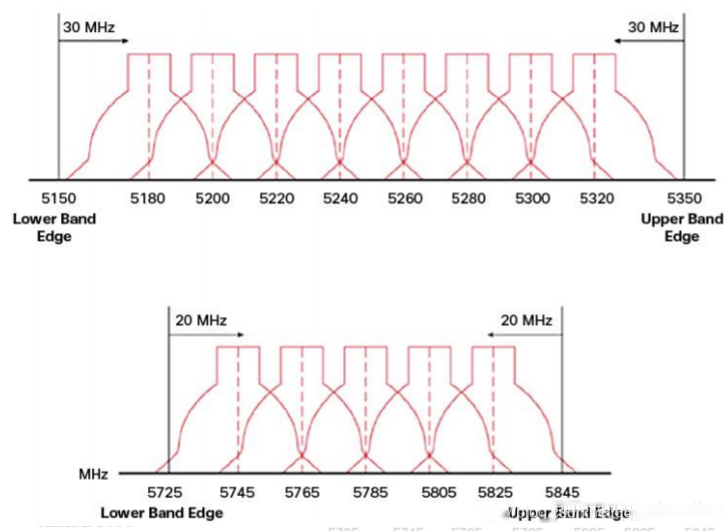
We can see that the number of non-overlapping channels in the 5GHz frequency band is more than that in 2.4GHz, and the probability of overlap or congestion is relatively small.
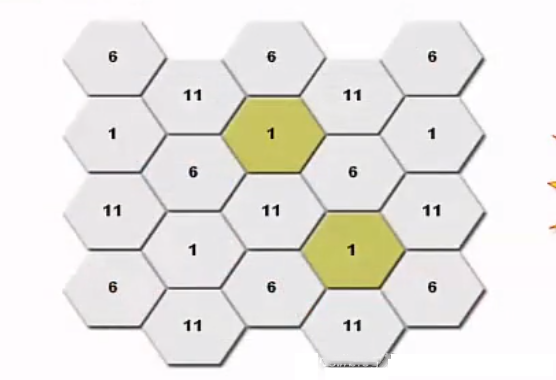
WLAN Channel Selection Principles
In the channel selection principle of deploying APs or routers, try to use independent channels, and physically adjacent APs or routers should choose different independent channels as much as possible to reduce interference between channels. As shown in the figure below (each hexagon represents a router or AP):
Signal Introduction
Identification method of signal strength: power and decibels.
dB is used to measure the ratio of the measured power to a certain basic power. Its value is equal to the ratio of the measured power to the reference power, taking the base 10 logarithm and multiplying it by 10. When the basic power is 1mw, the dB value is expressed in dBm, and the measured power (dB) = 10 * lg (measurement power mw).
For example, if the indoor AP power is 100mw, the maximum signal strength is 20dBm=10*lg^100.
When the wireless signal passes through an obstacle, the waveform of the wireless signal changes, that is, the wireless signal is attenuated. According to the different materials of the obstacle, the degree of attenuation of the signal is different, among which metal and concrete have the greatest impact.
Multipath propagation occurs when a signal travels more than one path from its origin to its destination. It is because some signals directly reach the endpoint, while other signs are reflected by obstacles to reach the endpoint. In this way, some signals are delayed and go through a long path before reaching the endpoint, and the phase also changes. Signals passing through different paths are at the receiving end Superposition creates multipath distortion.
Signal Transmission Characteristics – Electromagnetic Interference
- The repeated coverage of different network systems will cause mutual signal interference and channel interference.
- Same frequency and adjacent frequency interference between devices in the same network system.
- Interference with other devices operating on the same channel as the WLAN device.
